前言
编程中常见的加密算法有以下几种,它们在不同场景中分别有应用。除信息摘要算法外,其它加密方式都会需要密钥。
- 信息摘要算法
- 对称加密算法
- 非对称加密算法
密钥
密钥(key,又常称金钥)是指某个用来完成加密、解密、完整性验证等密码学应用的秘密信息。
密钥分类
- 加解密中的密钥:对称加密中共享相同的密钥,非对称加密中分公钥和私钥,公钥加密私钥解密。
- 消息认证码和数字签名中的密钥:在消息认证码中,消息发送方和接收方使用共享密钥进行认证。在数字签名中,签名使用私钥,而验证使用公钥。
- 会话密钥和主密钥:每次通信只使用一次的密钥称为会话密钥(session key)。相对于会话密钥,重复使用的密钥称为主密钥(master key)。
密钥和密码
密码一般是由用户生成,具有可读性,可以记忆和存储,常用于软件管理,而密钥是供实现加密算法的软件使用,不需要具备可读性(不过在编程中为了方便阅读都进行Base64)。我们也可以通过密码来生成密钥。
密钥管理
-
生成密钥:可以用随机数生成密钥,也可以用口令生成密钥。
-
配送密钥:可采用事先共享密钥、使用密钥分配中心、使用公钥密码、使用Diffie-Hellman密钥交换。
-
更新密钥
-
保存密钥
-
作废密钥
密钥生成
jdk 中 jce (Java Cryptography Extension) 包含了加密相关的所有API。
生成对称加密算法的密钥
| |
生成对称非对称加密算法的密钥
| |
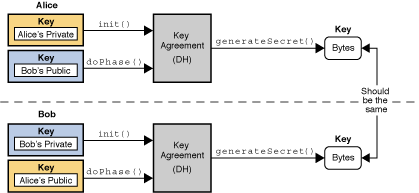
密钥协商(Diffie-Hellman)
密钥协商是一种协议,两方或多方在通过该协议建立相同的共享密钥,然后通讯内容进行对称加密传输,而不需要交换密钥。
大致过程:每一方生成一个公私钥对并将公钥分发给其它方,当都获得其他方的公钥副本后就可以离线计算共享密钥。
Java中提供了 KeyAgreement 可以实现密钥协商。
- Alice 和 Bob 分别用他们的私钥初始化自己的密钥协商对象
KeyAgreement,调用init()方法; - 然后将通信的每一方的公钥 传入执行
doPhase(Key key, boolean lastPhase); - 各方生成共享密钥
generateSecret()。
| |
信息摘要算法
信息摘要算法又叫加密散列算法,加密过程不需要密钥,常见的加密散列算法有MD系列和SHA系列。
一个理想的加密散列函数应该具备以下特性:
- 任何信息传入后,输出的总是长度固定;
- 消息摘要看起来是“随机的”,这样根据原始信息就很难推测出值;
- 好的散列函数碰撞概率应该极低,也就是不同信息传入后得到相同值的概率;
MD系列
MD5信息摘要算法(MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm),一种被广泛使用的加密散列函数,输出出一个128位(16字节)的散列值(hash value),MD5最初设计为加密散列函数,而目前发现它存在大量漏洞,所以不建议直接用作加密,不过在非加密场景下如:数据完整性校验,文件完整性校验它仍然有广泛的应用。
| |
SHA系列
安全散列算法(Secure Hash Algorithm,缩写为SHA)是一个加密散列函数家族,是FIPS(美国联邦信息处理标准)所认证的安全散列算法。能计算出一个数字消息所对应到的,长度固定的字符串(又称消息摘要)的算法。且若输入的消息不同,它们对应到不同字符串的机率很高。
它们分别包含 SHA-0、SHA-1、SHA-2、SHA-3,其中 SHA-0、SHA-1 输出长度是160位,SHA-2 包含 SHA-224、SHA-256、SHA-384、SHA-512、SHA-512/224、SHA-512/256,我们平时常用 SHA-256 。
| |
对称加密算法
对称加密算法,双方持有相同密钥进行加解密,常见的对称加密算法:DES 3DES AES128 AES192 AES256。理解对称加密需要先明白下面几个概念:
- 分组密码模式:将明文切割进行加密,再将密文拼接到一起。比如AES中会将明文数据切割为大小16字节的数据块,最后一块不够16字节时,使用Padding模式进行补充。
- 填充(Padding):它有三种模式PKCS5、PKCS7和NOPADDING,PKCS5用缺少的字节数来填充,比如缺少5个字节就填充5个数字5,PKCS7缺少的字节数用0来填充。如果数据刚好是16的整数倍,PKCS5和PKCS7会再补充一个16字节数据来区分填充和有效数据,NOPADDING模式不需要填充。
- 初始化向量:初始向量IV的作用是使加密更加安全可靠,在分组密码模式下IV大小对应数据块长度。
- 加密模式:四种加密模式分别是:ECB(电子密码本模式)、CBC(密码分组链接模式)、CFB、OFB。ECB模式是仅仅使用明文和密钥来加密数据,所以该模式下不需要Padding,安全性也较弱,CBC模式数据分块并且使用传入IV依次进行异或操作,安全性也相对较高,所以目前一般都选择CBC模式。
- 加密密钥:不同加密算法密钥长度不同,比如:DES 默认长度56位,3DES默认长度168位,也支持128位,AES默认128位,也支持192位,256位。我们一般根据密码生成密钥,密码长度需要满足算法密钥长度。
DES
DES 是对称加密算法领域中的典型算法,因为密钥默认长度为56 bit,所以密码长度需要大于 8 byte,DESKeySpec 取前 8 byte 进行密钥制作。
| |
3DES
3DES(即Triple DES)。是DES算法的加强,它使用3条56位的密钥对数据进行三次加密。它以DES为基本模块,通过组合分组方法设计出分组加密算法。比起最初的DES,3DES更为安全。密钥默认长度 168 bit, 密码需要大于24 byte,IV 是 8 byte 的随机数字和字母数组。
| |
AES
AES 高级数据加密标准,能够有效抵御已知的针对DES算法的所有攻击,默认密钥长度为128 bit,还可以供选择 192 bit,256 bit。AES-128 AES-192 AES-256
默认 AES-128 ,使用 PBEKeySpec 生成固定大小的密钥。
| |
使用 AES-256 时可能会出现下面异常:
|
|
JDK 1.8.0_161 及以上版本默认已经启用无限强度加密:
| |
JDK 1.8.0_161以前版本需要手动安装 jce 策略文件(下载地址)
非对称加密算法
非对称加密使用一对密钥,公钥用作加密,私钥则用作解密。关于密钥大小,截至2020年,公开已知的最大RSA密钥是破解的是829位的RSA-250,建议至少使用 2048 位密钥。
| |